US Naval Officer Ranks

Introduction to US Naval Officer Ranks

The United States Navy is one of the largest and most advanced naval forces in the world, with a complex system of ranks and insignia to denote the level of authority and responsibility held by each officer. Understanding the different ranks within the US Navy is essential for both current and aspiring naval officers, as well as for those interested in the inner workings of the naval service. In this article, we will delve into the various officer ranks within the US Navy, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and insignia.
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Commissioned officers in the US Navy are responsible for leading and managing enlisted personnel, as well as making key decisions regarding operations, strategy, and personnel management. The commissioned officer ranks in the US Navy, in order of increasing seniority, are: * Ensign (O-1) * Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2) * Lieutenant (O-3) * Lieutenant Commander (O-4) * Commander (O-5) * Captain (O-6) * Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (O-7) * Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (O-8) * Vice Admiral (O-9) * Admiral (O-10)
Warrant Officer Ranks

Warrant officers in the US Navy are technical experts who have risen through the ranks of the enlisted personnel. They possess specialized knowledge and skills, and are responsible for providing guidance and support to commissioned officers. The warrant officer ranks in the US Navy, in order of increasing seniority, are: * Warrant Officer 1 (W-1) * Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2) * Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3) * Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4) * Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5)
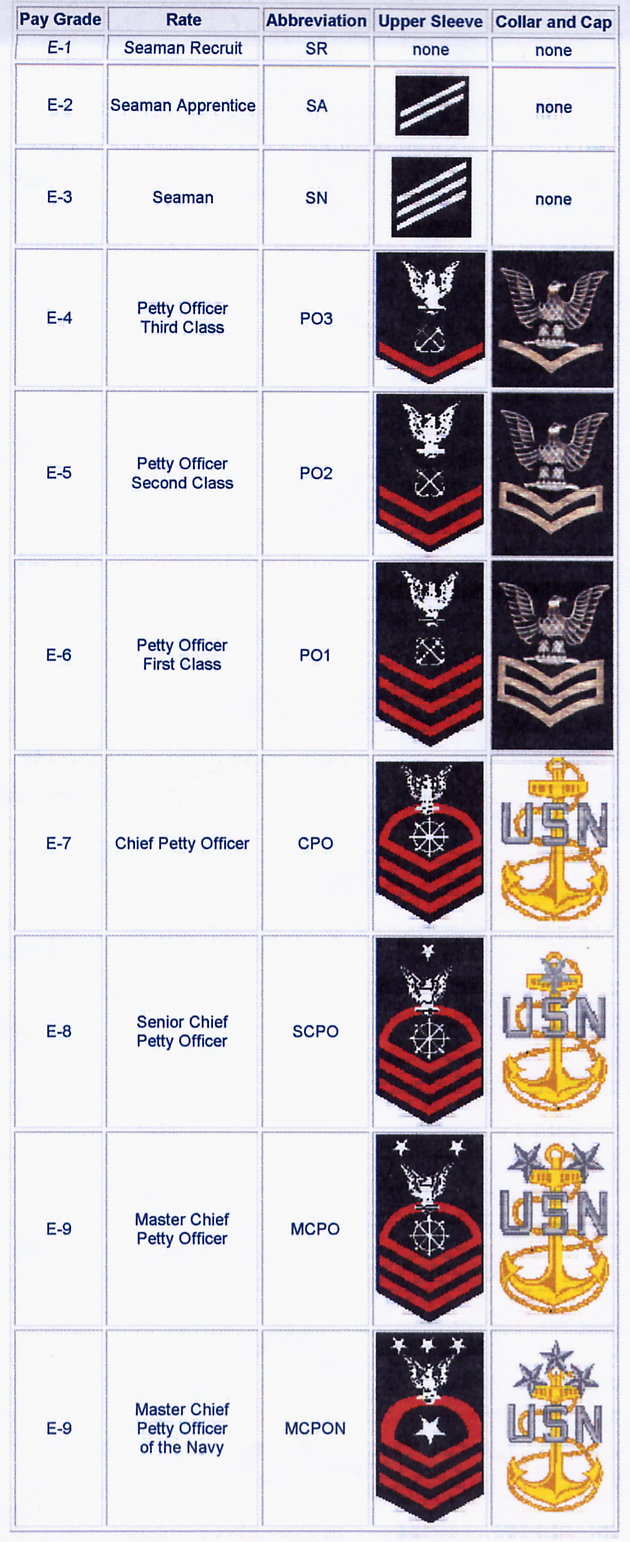
Enlisted Ranks

Although not technically considered officer ranks, enlisted personnel play a crucial role in the functioning of the US Navy. Enlisted ranks, in order of increasing seniority, are: * Seaman Recruit (E-1) * Seaman Apprentice (E-2) * Seaman (E-3) * Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) * Petty Officer Second Class (E-5) * Petty Officer First Class (E-6) * Chief Petty Officer (E-7) * Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8) * Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9)
🚨 Note: The ranks and insignia of the US Navy are subject to change, and it is essential to consult official sources for the most up-to-date information.
Rank Insignia

The US Navy uses a combination of stripes, stars, and other devices to denote the rank of an officer. The insignia for each rank is as follows:
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Ensign | One gold stripe |
| Lieutenant Junior Grade | One gold stripe with a gold star |
| Lieutenant | Two gold stripes |
| Lieutenant Commander | Two and a half gold stripes |
| Commander | Three gold stripes |
| Captain | Four gold stripes |
| Rear Admiral (Lower Half) | One gold star with one gold stripe |
| Rear Admiral (Upper Half) | One gold star with two gold stripes |
| Vice Admiral | Three gold stars |
| Admiral | Four gold stars |

Key Responsibilities and Roles

Each rank within the US Navy carries distinct responsibilities and roles. Some of the key duties associated with each rank include: * Leading and managing personnel: Commissioned officers are responsible for leading and managing enlisted personnel, as well as making key decisions regarding operations, strategy, and personnel management. * Providing technical expertise: Warrant officers provide technical guidance and support to commissioned officers, leveraging their specialized knowledge and skills. * Executing operations: Enlisted personnel play a crucial role in executing the day-to-day operations of the US Navy, from maintaining equipment to conducting missions.
In summary, the US Naval officer ranks are a complex system that denotes the level of authority, responsibility, and expertise held by each individual. By understanding the different ranks, insignia, and responsibilities, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the inner workings of the US Navy and the important role it plays in defending the nation.
The main points discussed in this article can be summarized as follows: * The US Navy has a complex system of ranks and insignia to denote the level of authority and responsibility held by each officer. * Commissioned officers are responsible for leading and managing enlisted personnel, as well as making key decisions regarding operations, strategy, and personnel management. * Warrant officers provide technical expertise and support to commissioned officers, leveraging their specialized knowledge and skills. * Enlisted personnel play a crucial role in executing the day-to-day operations of the US Navy.
What is the highest rank in the US Navy?
+
The highest rank in the US Navy is Admiral (O-10), which is a four-star rank.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?

+
Commissioned officers are responsible for leading and managing enlisted personnel, while warrant officers provide technical expertise and support to commissioned officers.
What is the role of enlisted personnel in the US Navy?

+
Enlisted personnel play a crucial role in executing the day-to-day operations of the US Navy, from maintaining equipment to conducting missions.



