Persian Gulf Location World Map

Introduction to the Persian Gulf

The Persian Gulf, also known as the Arabian Gulf, is a vital body of water located in the Middle East. It is connected to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea through the Strait of Hormuz. The Persian Gulf is bounded by several countries, including Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and Oman. The region is known for its rich oil reserves, making it a significant player in the global energy market.
Geographical Location
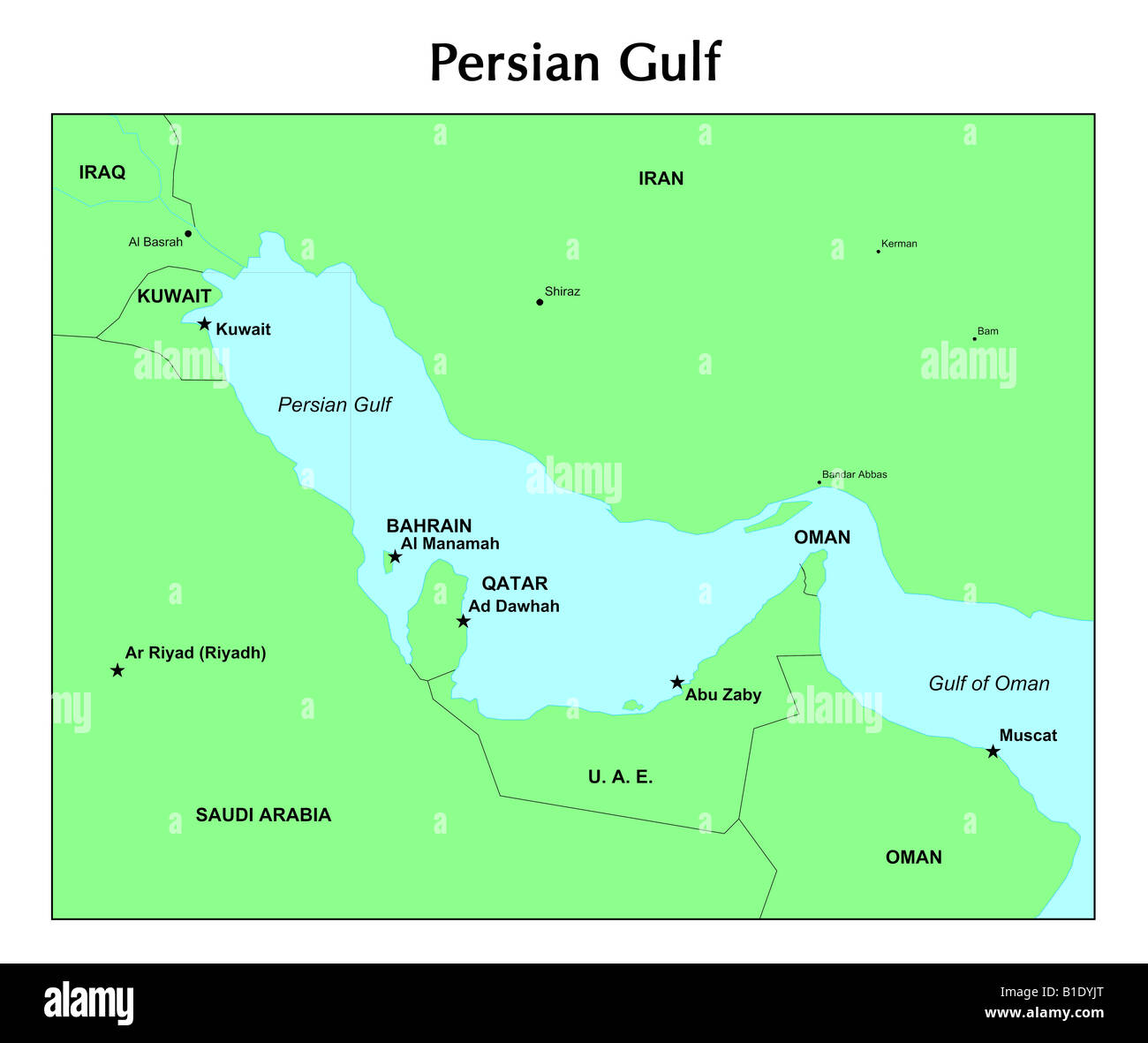
The Persian Gulf is situated in the southwestern part of Asia, with a total area of approximately 241,000 square kilometers. It stretches for about 990 kilometers from the Shatt al-Arab river, which forms the border between Iran and Iraq, to the Strait of Hormuz. The gulf’s width varies from 200 to 320 kilometers, with an average depth of around 35 meters. The Strait of Hormuz, which connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman, is a critical waterway, as it allows for the transportation of oil and other goods between the region and the rest of the world.
Countries Bordering the Persian Gulf

There are eight countries that border the Persian Gulf: * Iran * Iraq * Kuwait * Saudi Arabia * Qatar * United Arab Emirates * Oman * Bahrain (via a small island in the gulf)
Each of these countries has a unique relationship with the Persian Gulf, with some relying heavily on its oil reserves, while others have developed significant maritime trade and tourism industries.
Economic Importance

The Persian Gulf is of immense economic importance, due to its vast oil reserves. The region is home to some of the largest oil-producing countries in the world, including Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Iraq. The gulf’s oil reserves are estimated to be around 675 billion barrels, which is approximately 48% of the world’s total oil reserves. The oil industry has driven the economies of many countries in the region, with oil exports being a significant source of revenue.
Environmental Concerns

The Persian Gulf is facing several environmental concerns, including: * Pollution: The gulf is prone to oil spills, which can have devastating effects on the marine ecosystem. * Overfishing: The gulf’s fish stocks are being depleted due to overfishing, which can have long-term consequences for the region’s food security. * Climate Change: Rising temperatures and sea levels are affecting the gulf’s coastal ecosystems and marine life.
🌎 Note: The Persian Gulf's environmental concerns are a pressing issue, and it requires the cooperation of all countries in the region to address these challenges.
Cultural Significance

The Persian Gulf has a rich cultural heritage, with a history dating back thousands of years. The region is home to several ancient civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Persians. The gulf’s strategic location has made it an important center for trade and commerce, with many countries in the region developing significant cultural and economic ties.
| Country | Capital City | Population (2020 est.) |
|---|---|---|
| Iran | Tehran | 83 million |
| Iraq | Baghdad | 40 million |
| Kuwait | Kuwait City | 4 million |
| Saudi Arabia | Riyadh | 35 million |
| Qatar | Doha | 2.6 million |
| United Arab Emirates | Abu Dhabi | 9.5 million |
| Oman | Muscat | 5 million |

The Persian Gulf’s cultural significance extends beyond its economic importance, with the region being home to several UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the ancient city of Persepolis in Iran and the historic city of Muharraq in Bahrain.
In summary, the Persian Gulf is a vital region, with significant economic, cultural, and environmental importance. Its strategic location and rich oil reserves have made it a critical player in the global energy market, while its cultural heritage and historical significance have made it a fascinating region to explore. As the region continues to evolve, it is essential to address the environmental concerns and promote sustainable development to ensure the long-term prosperity of the Persian Gulf.
What is the significance of the Persian Gulf in the global energy market?

+
The Persian Gulf is home to some of the largest oil-producing countries in the world, making it a critical player in the global energy market. The region’s oil reserves are estimated to be around 675 billion barrels, which is approximately 48% of the world’s total oil reserves.
What are the environmental concerns facing the Persian Gulf?

+
The Persian Gulf is facing several environmental concerns, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. The region’s oil spills, overfishing, and rising temperatures and sea levels are affecting the gulf’s coastal ecosystems and marine life.
What is the cultural significance of the Persian Gulf?

+
The Persian Gulf has a rich cultural heritage, with a history dating back thousands of years. The region is home to several ancient civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Persians. The gulf’s strategic location has made it an important center for trade and commerce, with many countries in the region developing significant cultural and economic ties.



