Army Rank List In Order

Introduction to Army Ranks

The army rank list is a system of hierarchical relationships that define the roles and responsibilities of soldiers within the military. Understanding the army rank list is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or learning more about the structure of the army. In this article, we will explore the different ranks in the army, from the lowest to the highest, and provide information on the responsibilities and requirements for each rank.
Enlisted Ranks

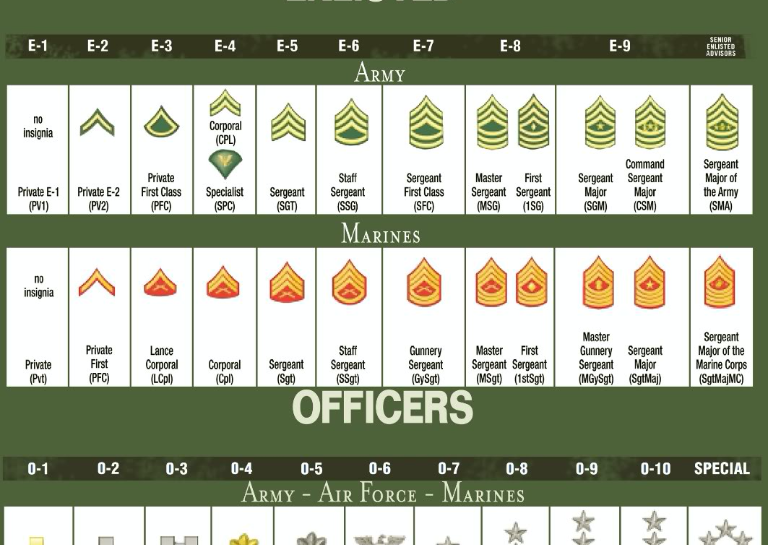
The enlisted ranks are the lowest ranks in the army, and they are the backbone of the military. Enlisted soldiers are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations of the army. The enlisted ranks are as follows: * Private (PVT) * Private Second Class (PV2) * Private First Class (PFC) * Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) * Sergeant (SGT) * Staff Sergeant (SSG) * Sergeant First Class (SFC) * Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG) * Sergeant Major (SGM) * Command Sergeant Major (CSM) * Sergeant Major of the Army (SMA)
Warrant Officer Ranks

Warrant officers are technical experts in their field and are responsible for providing guidance and advice to commanders. The warrant officer ranks are as follows: * Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) * Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) * Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) * Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) * Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5)
Officer Ranks

Officer ranks are the highest ranks in the army, and they are responsible for leading and commanding units. The officer ranks are as follows: * Second Lieutenant (2LT) * First Lieutenant (1LT) * Captain (CPT) * Major (MAJ) * Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) * Colonel (COL) * Brigadier General (BG) * Major General (MG) * Lieutenant General (LTG) * General (GEN)
Table of Army Ranks

The following table summarizes the army rank list:
| Rank | Pay Grade | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Private | E-1 | PVT |
| Private Second Class | E-2 | PV2 |
| Private First Class | E-3 | PFC |
| Specialist/Corporal | E-4 | SPC/CPL |
| Sergeant | E-5 | SGT |
| Staff Sergeant | E-6 | SSG |
| Sergeant First Class | E-7 | SFC |
| Master Sergeant/First Sergeant | E-8 | MSG/1SG |
| Sergeant Major | E-9 | SGM |
| Command Sergeant Major | E-9 | CSM |
| Sergeant Major of the Army | E-9 | SMA |
| Warrant Officer 1 | W-1 | WO1 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 2 | W-2 | CW2 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 3 | W-3 | CW3 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 4 | W-4 | CW4 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 5 | W-5 | CW5 |
| Second Lieutenant | O-1 | 2LT |
| First Lieutenant | O-2 | 1LT |
| Captain | O-3 | CPT |
| Major | O-4 | MAJ |
| Lieutenant Colonel | O-5 | LTC |
| Colonel | O-6 | COL |
| Brigadier General | O-7 | BG |
| Major General | O-8 | MG |
| Lieutenant General | O-9 | LTG |
| General | O-10 | GEN |

👮 Note: The army rank list may vary depending on the country and the specific branch of the military.
In terms of responsibilities, each rank has its own set of duties and expectations. Enlisted soldiers are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations of the army, while warrant officers provide technical expertise and guidance. Officers, on the other hand, are responsible for leading and commanding units.
To advance in rank, soldiers must meet certain requirements, such as completing training and education programs, demonstrating leadership and technical skills, and accumulating time in service. The promotion process typically involves a combination of these factors, as well as evaluations and recommendations from superiors.
In conclusion, understanding the army rank list is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or learning more about the structure of the army. By recognizing the different ranks and their corresponding responsibilities, individuals can better appreciate the complexity and hierarchy of the military.
What is the highest rank in the army?
+
The highest rank in the army is General (GEN).
What is the difference between an enlisted soldier and an officer?

+
Enlisted soldiers are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations of the army, while officers are responsible for leading and commanding units.
How do soldiers advance in rank?

+
Soldiers advance in rank by meeting certain requirements, such as completing training and education programs, demonstrating leadership and technical skills, and accumulating time in service.



