Blocking Signal Interference

Understanding Signal Interference

Signal interference is a common problem that can affect the quality and reliability of various signals, including wireless communications, radio frequencies, and even electronic devices. It occurs when an external signal or noise disrupts the original signal, causing errors, distortions, or complete loss of the signal. In today’s technology-driven world, signal interference can have significant consequences, ranging from dropped calls and slow internet speeds to malfunctions in critical systems.
Causes of Signal Interference

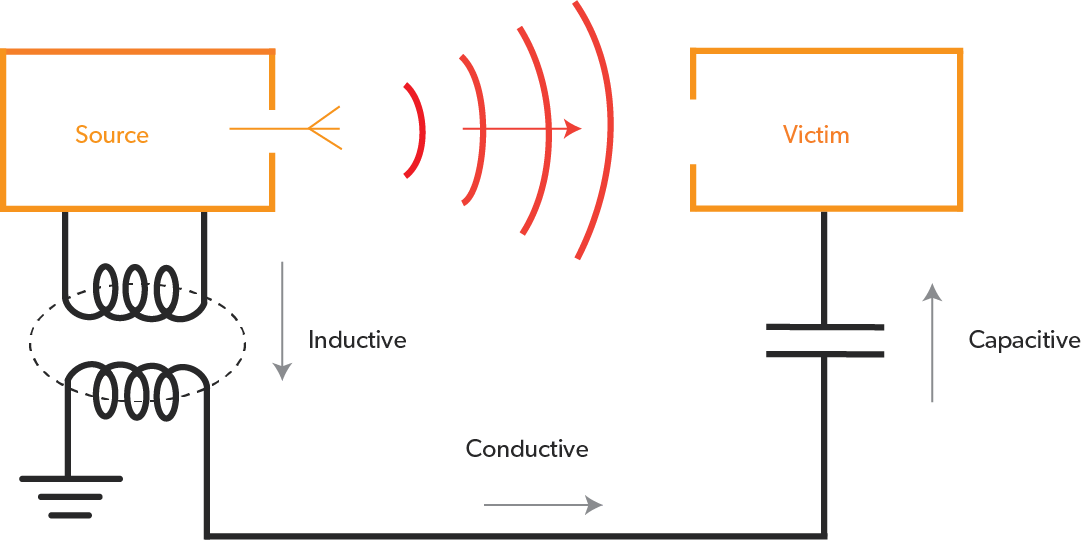
There are several causes of signal interference, including: * Physical barriers: Walls, mountains, and other physical obstacles can block or weaken signals. * Electromagnetic interference (EMI): Electronic devices, such as microwaves, fluorescent lights, and computers, can generate electromagnetic fields that interfere with signals. * Radio-frequency interference (RFI): Other wireless devices, such as cordless phones, baby monitors, and neighboring wireless networks, can cause RFI. * Atmospheric conditions: Weather conditions, such as heavy rain, fog, or solar activity, can affect signal strength and quality. * Device malfunctions: Faulty or poorly designed devices can generate interference, either intentionally or unintentionally.
Effects of Signal Interference

Signal interference can have significant effects on various aspects of our lives, including: * Communication: Dropped calls, poor voice quality, and slow internet speeds can be frustrating and affect productivity. * Navigation: Interference with GPS signals can cause errors in location tracking and navigation. * Safety: In critical systems, such as aviation and medical devices, signal interference can have life-threatening consequences. * Security: Interference with security systems, such as alarms and surveillance cameras, can compromise safety and security.
Methods for Blocking Signal Interference

To mitigate the effects of signal interference, several methods can be employed: * Shielding: Using materials with high electromagnetic absorption properties, such as copper or mu-metal, to block or absorb interfering signals. * Filtering: Implementing filters to remove unwanted frequencies and allow only the desired signal to pass through. * Frequency hopping: Switching between different frequencies to avoid interference from other devices. * Error correction: Using algorithms to detect and correct errors caused by signal interference. * Signal amplification: Boosting the signal strength to overcome interference.
Technologies for Blocking Signal Interference
Several technologies are available to block signal interference, including: * Signal jamming: Transmitting a signal that interferes with the interfering signal, effectively canceling it out. * Frequency-selective surfaces: Using materials that can filter out specific frequencies, allowing only the desired signal to pass through. * Meta-materials: Creating materials with tailored electromagnetic properties to block or absorb interfering signals. * Active cancellation: Using electronic circuits to generate a signal that cancels out the interfering signal.
📝 Note: When using signal jamming technologies, it is essential to ensure that they comply with relevant regulations and do not interfere with other critical systems.
Applications of Signal Interference Blocking
The ability to block signal interference has numerous applications in various fields, including: * Wireless communication: Improving the quality and reliability of wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi and cellular networks. * Aviation: Ensuring safe and reliable communication and navigation systems in aircraft. * Medical devices: Preventing interference with life-critical medical devices, such as pacemakers and insulin pumps. * Industrial control systems: Protecting critical infrastructure, such as power grids and manufacturing systems, from signal interference.
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Wireless communication | Improved signal quality, increased reliability, and faster data transfer rates |
| Aviation | Enhanced safety, improved navigation, and reduced risk of accidents |
| Medical devices | Prevention of life-threatening errors, improved patient safety, and reduced risk of device malfunction |
| Industrial control systems | Increased reliability, improved productivity, and reduced risk of system failures |

In summary, signal interference is a common problem that can have significant consequences in various aspects of our lives. Understanding the causes and effects of signal interference is crucial in developing effective methods for blocking it. By employing technologies such as shielding, filtering, and signal amplification, we can mitigate the effects of signal interference and improve the quality and reliability of various systems. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of blocking signal interference will only continue to grow, and it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments and advancements in this field.
What is signal interference, and how does it affect wireless communication?

+
Signal interference occurs when an external signal or noise disrupts the original signal, causing errors, distortions, or complete loss of the signal. In wireless communication, signal interference can lead to dropped calls, poor voice quality, and slow internet speeds.
What are some common causes of signal interference?
+
Common causes of signal interference include physical barriers, electromagnetic interference (EMI), radio-frequency interference (RFI), atmospheric conditions, and device malfunctions.
How can signal interference be blocked or mitigated?

+
Signal interference can be blocked or mitigated using methods such as shielding, filtering, frequency hopping, error correction, and signal amplification. Additionally, technologies such as signal jamming, frequency-selective surfaces, meta-materials, and active cancellation can be employed to block signal interference.



